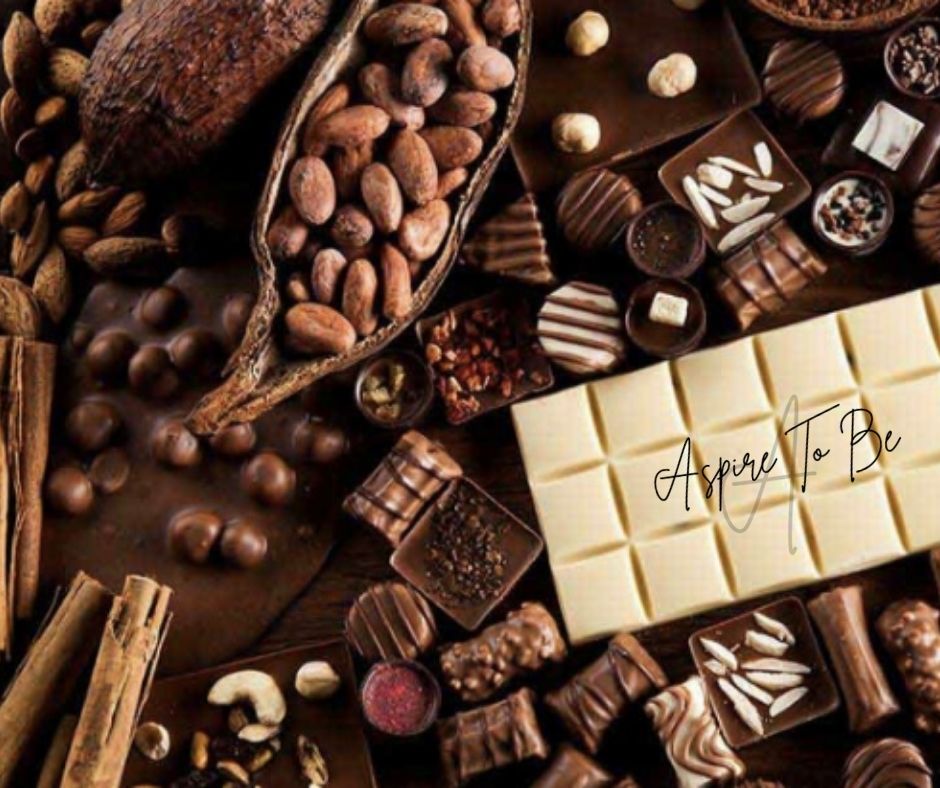
Let’s talk about chocolate and its benefits. Chocolate lowers the risk of heart disease and stroke, protects against free radicals damage, an effective cough suppressant, stomachs, and much more.
History:
Chocolate comes from the seeds of the cacao pod, which grows on the cacao tree. Theobroma cacao is native to the tropical rainforests of Central America, where it has grown for thousands of years. Around 2,000 years ago, the Maya have experienced cacao bean farmers and were fond of grinding them up for a refreshing hot beverage. There are three main varieties of cacao bean: Criollo from Latin America, Forastero from Africa, and Trinitario from the Caribbean. Forastero accounts for about 90 % of all cacao beans, with Criollo and Trinitario making up the rest.
Scientific research into chocolate is turning up some intriguing possibilities about its healthful nutrients, including improved immunity, greater longevity, and quicker recovery from intense exercise. Dark chocolate without unhealthy additives and sugar has been shown to lower the risk of cancer and stroke and lowers blood pressure as effectively as antioxidant-rich fruit and vegetables.
What Is It Good For:
Heart Health:
Moderate consumption protects the heart by thinning the blood in the same way as low-dose aspirin, while its beneficial flavonoids protect artery walls and lower blood pressure and cholesterol.
Immune Support:
Weight for weight has the same amount of antioxidants as red wine. These support overall immunity by boosting the response of antibodies and T-helper cells and strengthening the intestinal lining against invading microorganisms.
Digestion:
Studies show substances in dark chocolate help ease gastrointestinal upsets.
Eases Coughs:
One of the stimulants in cocoa, theobromine, has been shown to be more effective than codeine for soothing a sore throat.
Some Proven Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate
- Very Nutritious
- Powerful Source of Antioxidants
- May Improve Blood Flow and Lower Blood Pressure
- Raises HDL and Protects LDL From Oxidation
- May Reduce Heart Disease Risk
- May Protect Your Skin From the Sun
- Could Improve Brain Function

How Do I Get The Best From It?
Choose Organic:
At least 30 pesticides used in conventional cocoa so opt-out for organic.
Go Dark:
For the most antioxidants, choose semisweet or unsweetened chocolate with at least 70% of cocoa solids and less sugar. Milk chocolate contains fewer antioxidants.
A Little Of The Best:
Eating a little high-quality chocolate will be far more satisfying than a highly processed bar. Avoid bars with hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils.
Dark chocolate offers you a good mix of minerals, including:
- Magnesium
- Zinc
- Iron
- Phosphorus
- Copper
One-quarter cup of dark chocolate, about 1.5 oz or 2 large squares, contains:
- 142 calories
- 2 grams of protein
- 10 grams of fat
- 15 grams of carbohydrates
- 3 grams of fiber
- 11 grams of sugar
- 0 milligrams of cholesterol
- 0 milligrams of sodium
Cocoa Powder

Unsweetened Cocoa powder has twice the level of antioxidant polyphenols as processed dark chocolate and 4 times that of milk chocolate ( white chocolate contains no antioxidant).
Cocoa Beans

The catechin and epicatechin the antioxidants found in cocoa products are the same as those that give green tea its anti-cancer properties.
Cacao Nibs

Cacao nibs are dried, roasted, and crushed cacao, or cocoa, beans, which are used to make chocolate. Like the cocoa powder, they are high in antioxidants.
Dark Chocolate

Studies show that people who eat dark chocolate regularly have a lower risk of heart disease and stroke.
Conclusion
You might ask is dark chocolate good for you? Take a look at the dark chocolate nutrition facts and it’s easy to see why this incredible ingredient is packed with health benefits. Just remember that moderation is always key.